
color guide blood collection tubes
The standardized color-coding system for blood collection tubes ensures accurate specimen collection, reducing errors and improving patient care. Each tube color corresponds to specific additives and tests, guiding healthcare professionals in selecting the correct tube for various laboratory analyses, from routine blood work to specialized diagnostics;
1.1 Overview of the Importance of Tube Colors
Tube colors are crucial for accurate blood specimen collection, ensuring the correct additives are used for specific tests. This standardized system minimizes errors, improves efficiency, and maintains specimen integrity, enabling reliable laboratory results and better patient care.
1.2 Brief History of Standardized Color Coding
The standardization of blood collection tube colors emerged in the mid-20th century to reduce errors and enhance consistency in laboratory testing. This system ensures clarity in specimen collection, aligning tube colors with specific additives and tests, thereby improving patient safety and diagnostic accuracy.
Common Blood Collection Tube Colors and Their Uses
Blood collection tubes are color-coded to indicate specific additives and uses, ensuring accurate specimen collection for various laboratory tests, from blood chemistry to coagulation studies.
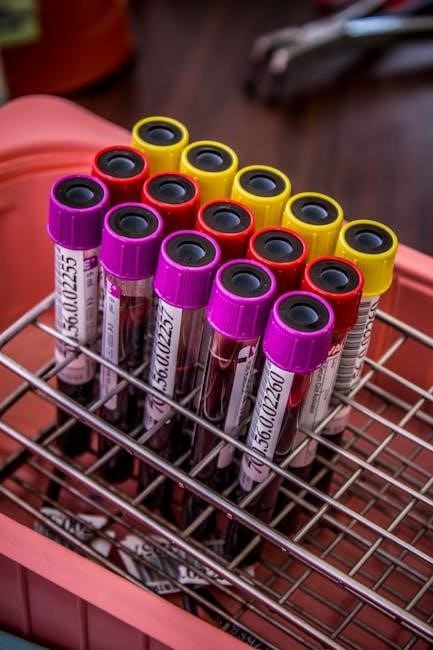
2.1 Red Tubes: Blood Chemistry Tests and Serology
Red tubes, containing no additives, allow blood to clot naturally for serum separation. They are used for blood chemistry tests, serology, and blood bank studies, requiring 15-30 minutes for clotting before centrifugation.
2.2 Gold (SST) Tubes: Serum Separation and Common Tests
Gold (SST) tubes contain clot activators and gel for serum separation, making them ideal for blood chemistry tests, infectious disease serology, and drug level monitoring. They require five inversions to mix additives, with a 30-minute clotting time before centrifugation. They are commonly used in clinical settings for effective serum separation.
2.3 Lavender Tubes: EDTA for Hematology Tests
Lavender tubes contain EDTA, an anticoagulant that prevents clotting by binding calcium ions. They are primarily used for hematology tests, such as complete blood counts (CBC), blood typing, and coagulation studies. The tube should be inverted 8-10 times post-collection to ensure proper mixing of blood with EDTA for accurate test results.
2.4 Light Blue Tubes: Coagulation Studies
Light blue tubes contain sodium citrate, an anticoagulant that prevents clotting by binding calcium ions. They are used for coagulation studies, such as prothrombin time (PT), international normalized ratio (INR), and fibrinogen testing. A discard tube may be required if drawn first to ensure accurate results for these critical tests.
2.5 Green Tubes: Sodium or Lithium Heparin for Plasma Tests
Green tubes contain sodium or lithium heparin, anticoagulants that prevent clotting by inhibiting thrombin formation. They are used for plasma tests, such as clinical chemistry and toxicology studies, ensuring accurate blood analysis by maintaining sample integrity without clot formation.
2.6 Other Tube Colors: Pink, Royal Blue, Tan, and Yellow
Pink tubes often contain EDTA for blood typing and are used in immunohematology. Royal blue tubes are typically used for coagulation studies, while tan tubes may contain sodium polyanethol sulfonate for certain tests. Yellow tubes are commonly used for blood culture collection to detect infections and identify pathogens effectively.
The Order of Draw: Best Practices for Blood Collection
The order of draw ensures accurate test results by preventing cross-contamination of additives. Blood cultures are drawn first, followed by royal blue, red, SST, green, tan, yellow, pink, pearl, and lavender tubes.
3.1 Importance of the Order of Draw
The order of draw is critical to prevent contamination and ensure accurate test results; Following the sequence avoids mixing additives between tubes, maintaining specimen integrity and reliability for laboratory analysis. Proper adherence reduces errors, ensuring patient safety and reliable diagnostic outcomes.
3.2 Standard Sequence for Tube Collection
The standard sequence begins with blood cultures, followed by coagulation tubes, SST/gold, red, green, tan, yellow, pink, pearl, and lavender. This order prevents cross-contamination of additives, ensuring the integrity of each sample and accurate laboratory results for various diagnostic tests and procedures.
3.3 Special Considerations for Blood Cultures
Blood cultures are always collected first to minimize contamination risks. Use both aerobic and anaerobic bottles, filling each with 8-10 mL of blood. Avoid overfilling to maintain the blood-to-broth ratio. Use a butterfly needle for difficult venipuncture. Proper technique ensures accurate detection of pathogens in suspected infections.

Tube Additives and Their Functions
Tube additives like clot activators, anticoagulants, and gels ensure proper blood sample processing. They prevent clotting, promote serum separation, and maintain sample integrity for accurate laboratory testing.
4.1 Clot Activators and Gel for Serum Separation
Clot activators and gel in tubes like gold (SST) facilitate rapid serum separation. After blood collection, the activator promotes clotting, while the gel forms a barrier, separating serum from blood cells for accurate testing and analysis.
4.2 Anticoagulants: EDTA, Sodium Citrate, and Heparin
EDTA prevents clotting by binding calcium, ideal for hematology tests like CBCs. Sodium citrate is used in coagulation studies, such as PT/INR. Heparin, found in green tubes, inhibits clotting for plasma tests; Each anticoagulant ensures accurate results by preventing unwanted clot formation during sample collection and analysis.
4.3 No Additive Tubes for Whole Blood Samples
No additive tubes allow blood to clot naturally, separating serum for chemistry tests. They contain no anticoagulants or clot activators, making them suitable for serology, blood bank studies, and other tests requiring whole blood samples without interference from additives, ensuring accurate and reliable laboratory results.

Specialized Blood Collection Tubes
Specialized blood collection tubes include blood culture bottles for detecting infections, pediatric tubes for smaller samples, and other unique designs for specific diagnostic needs, ensuring precise sample handling.
5.1 Blood Culture Bottles
Blood culture bottles are specialized tubes used to detect infections like bacteremia or sepsis. They contain media to support microbial growth, with aerobic and anaerobic bottles for comprehensive testing. Proper collection techniques, including order of draw and needle changes, are crucial to avoid contamination and ensure accurate results for timely patient treatment. Always follow sterile procedures to maintain sample integrity and reliability.
5.2 Pediatric and Low-Volume Tubes
Pediatric and low-volume tubes are designed for infants and children, requiring smaller blood samples. Available in 2mL or less, these tubes use the same color coding as standard tubes but minimize the volume needed, reducing discomfort and stress. They ensure accurate results with minimal sample size, ideal for young patients.
5.3 Light Blue Tubes for Coagulation Tests
Light blue tubes contain sodium citrate, an anticoagulant preventing clotting for coagulation studies. Used for tests like PT, INR, and fibrinogen, they ensure accurate blood clotting assessments. Proper inversion mixes the additive with blood, crucial for reliable coagulation results in clinical settings.

Practical Considerations for Tube Handling
Proper tube inversion ensures additive mixing, while adhering to clotting times maintains specimen integrity. Correct storage and transport prevent contamination and ensure accurate test results, avoiding pre-analytical errors.
6.1 Tube Inversion and Mixing
Tube inversion ensures proper mixing of blood with additives. Gold (SST) tubes require 5 inversions, while others may need up to 10. Proper mixing prevents clotting or ensures serum separation, depending on the tube type, guaranteeing accurate test results and maintaining specimen integrity for reliable laboratory analysis.
6.2 Clotting Time and Specimen Integrity
Clotting time varies by tube type, with red tubes requiring 15-30 minutes. Proper clotting ensures serum separation, maintaining specimen integrity. Incorrect handling can lead to hemolysis or clotting failures, compromising test accuracy and patient care, emphasizing the need for adherence to standardized blood collection procedures and guidelines.
6.3 Storage and Transport Guidelines
Collected blood samples must be stored at appropriate temperatures, either room temperature or refrigerated, depending on the test requirements. Timely transport to the laboratory is crucial to maintain specimen integrity. Proper packaging and handling during transport prevent hemolysis or contamination, ensuring accurate test results and reliable patient care outcomes.
Common Tests Associated with Each Tube Color
Each tube color is linked to specific tests: red for chemistry and serology, gold for serum separation, lavender for hematology, light blue for coagulation, and green for plasma tests.
7.1 Chemistry Tests and Drug Levels
Gold (SST) tubes are preferred for serum separation, used in tests like albumin and alkaline phosphos. Red tubes are used for blood chemistry and serology. Green tubes with lithium heparin are ideal for plasma tests and drug levels, ensuring accurate results with proper mixing and no clotting.
7.2 Hematology Tests: CBC and Beyond
Lavender tubes with EDTA are essential for hematology tests like CBC, differential counts, and reticulocyte tests. The anticoagulant prevents clotting, preserving blood cells for accurate analysis. Proper mixing through inversion ensures reliable results for diagnosing anemia, infection, and blood disorders.
7.3 Coagulation Studies: PT, INR, and Fibrinogen
Light blue tubes with sodium citrate are used for coagulation studies like PT, INR, and fibrinogen. The anticoagulant prevents clotting, ensuring accurate blood coagulation profiles. Proper tube inversion and discard of the first draw when light blue is first ensure reliable results for diagnosing bleeding or clotting disorders.
Clinical Relevance of Proper Tube Selection
Proper tube selection ensures accurate test results, crucial for correct diagnosis and treatment. Incorrect choices can lead to errors, impacting patient care and outcomes significantly.
8.1 Impact on Test Accuracy and Patient Care
Proper blood collection tube selection is critical for accurate laboratory results. Incorrect tube choices can lead to inaccurate test outcomes, which may result in misdiagnosis or inappropriate treatment, ultimately affecting patient care and clinical decision-making processes.
8.2 Reducing Errors in Laboratory Testing
Using the correct blood collection tube ensures accurate test results by preventing sample contamination or degradation. Proper tube selection avoids errors, ensuring specimen integrity and reliable laboratory outcomes, which are essential for accurate diagnoses and effective patient care.
Future Trends in Blood Collection Tubes
Advancements in tube technology include microsampling, automated systems, and eco-friendly designs, enhancing efficiency and sustainability. These innovations aim to improve specimen collection and reduce environmental impact.
9.1 Innovations in Tube Technology
Innovations in blood collection tubes include miniaturized designs for pediatric and low-volume sampling, anti-clotting agents, and eco-friendly materials. These advancements enhance patient comfort, reduce waste, and improve the accuracy of laboratory results while maintaining the integrity of the blood samples collected.
9.2 Advances in Additive Development
Recent advancements in additives include improved clot activators, stabilizers, and anticoagulants, enhancing specimen quality and test accuracy. Innovations like faster mixing agents and clotting times have optimized blood sample preparation, ensuring reliable diagnostic results while maintaining the integrity of the collected specimens for various laboratory analyses.
Understanding blood collection tube color coding is essential for accurate testing and patient care. Proper tube selection ensures reliable results, making it a cornerstone of modern healthcare diagnostics and treatment.
10.1 Summary of Key Points
Blood collection tube color coding ensures accurate specimen collection and laboratory testing. Each color represents specific additives and tests, guiding healthcare professionals to select the right tube. Proper tube selection, order of draw, and handling practices are critical for reliable results, directly impacting patient diagnosis, treatment, and overall care quality.
10.2 Importance of Adhering to Guidelines
Adhering to blood collection guidelines ensures accurate test results, reduces errors, and maintains patient safety. Proper tube selection, order of draw, and handling practices prevent specimen contamination and mix-ups, directly impacting the reliability of laboratory tests and subsequent medical decisions.
Related posts:
Archives
- February 2026
- January 2026
- December 2025
- November 2025
- October 2025
- September 2025
- August 2025
- July 2025
- June 2025
- May 2025
- April 2025
- March 2025
- February 2025
- January 2025
- December 2024
- November 2024
- October 2024
- September 2024
- August 2024
- July 2024
- June 2024
- May 2024
- April 2024
- March 2024
- February 2024
- January 2024
- December 2023
- November 2023
- October 2023
- September 2023
- August 2023
- July 2023
- June 2023
- May 2023
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.